Australian Cattle Dog
General Information - Australian Cattle Dog
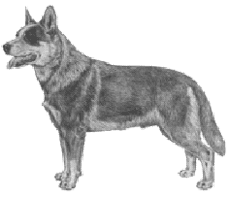
Group:
Working
Size:
medium
Lifespan:
10-13 years
Exercise:
medium
Grooming:
low
Trainability:
very high
Watchdog ability:
very high
Protection ability:
high
Area of Origin:
Australia
Date of Origin:
1800s
Other Names:
Queensland Heeler,Blue Heeler, Halls Heeler
Original Function:
cattle herding
History
The Australian Cattle Dog, originally known as the Queensland Blue Heeler, was specifically created by early ranchers in Australia who needed a dog capable of handling sheep and cattle in the wide open spaces of that country. (A Heeler is a dog that works the cattle by nipping at their heels.) In the 1830s, a hardy, yet noisy, breed known as the Smithfield was crossed with the quiet, steadfast wild dog of Australia, the Dingo. The result was a quieter dog but also more unruly and a strong biter. This dog was crossed again with other breeds such as the Blue Merle Smooth Collie to regain control, the Dalmatian to regain temperament, especially around horses, and the Australian Kelpie to regain herding instincts. The final result was a manageable herding and working dog with superb temperament and intelligence, able to work tirelessly over large areas in harsh conditions and very high temperatures, and in wide or closed spaces. The breed was officially recognised in 1903 by the New South Wales Kennel Club, when it was renamed the Australian Cattle Dog. It remains still today as a true and prized herding dog in Australia as well as in North America. The breed requires plenty of outdoor exercise.
Temperament
Independent and obedient, Australian Cattle Dogs are sometimes suspicious of people they don't know. Australian Cattle Dogs are loyal and tireless hard workers who are devoted to protecting their owners, herd and property.
Upkeep
The Australian Cattle Dog was bred to be active and tireless. This dog needs a lot of physical and mental activity, more than a simple walk on a leash can provide. A good jog or long workout, coupled with obedience lessons or other intellectual challenges, is essential every day. It is happiest when it has a job to perform, and especially when that job is herding. The Australian Cattle Dog can live outdoors in temperate to cool climates. It is unsuited for apartment life. Its coat needs brushing or combing weekly to remove dead hairs.
Australian Cattle Dog
A breed standard is the guideline which describes the ideal characteristics, temperament, and appearance of a breed and ensures that the breed is fit for function with soundness essential. Breeders and judges should at all times be careful to avoid obvious conditions and exaggerations, as well as being mindful of features which could be detrimental in any way to the health, welfare or soundness of this breed.
Breed Standard - Australian Cattle Dog
 Country of Origin:
Country of Origin: Australia
General Appearance: The general appearance is that of a strong compact, symmetrically built working dog, with the ability and willingness to carry out his allotted task however arduous. Its combination of substance, power, balance and hard muscular condition must convey the impression of great agility, strength and endurance. Any tendency to grossness or weediness is a serious fault.
Characteristics: As the name implies the dog's prime function, and one in which he has no peer, is the control and movement of cattle in both wide open and confined areas. Always alert, extremely intelligent, watchful, courageous and trustworthy, with an implicit devotion to duty making it an ideal dog.
Temperament: The Cattle Dog's loyalty and protective instincts make it a self:appointed guardian to the Stockman, his herd and his property. Whilst naturally suspicious of strangers, must be amenable to handling, particularly in the Show ring. Any feature of temperament or structure foreign to a working dog must be regarded as a serious fault.
Head and Skull: The head is strong and must be in balance with other proportions of the dog and in keeping with its general conformation. The broad skull is slightly curved between the ears, flattening to a slight but definite stop. The cheeks muscular, neither coarse nor prominent with the underjaw strong, deep and well developed. The foreface is broad and well filled in under the eyes, tapering gradually to form a medium length, deep, powerful muzzle with the skull and muzzle on parallel planes. The lips are tight and clean. Nose black.
Eyes: The eyes should be of oval shape and medium size, neither prominent nor sunken and must express alertness and intelligence. A warning or suspicious glint is characteristic when approached by strangers. Eye colour, dark brown.
Ears: The ears should be of moderate size, preferably small rather than large, broad at the base, muscular, pricked and moderately pointed neither spoon nor bat eared. The ears are set wide apart on the skull, inclining outwards, sensitive in their use and pricked when alert, the leather should be thick in texture and the inside of the ear fairly well furnished with hair.
Mouth: The teeth, sound, strong and evenly spaced, gripping with a scissor:bite, the lower incisors close behind and just touching the upper. As the dog is required to move difficult cattle by heeling or biting, teeth which are sound and strong are very important.
Neck: The neck is extremely strong, muscular, and of medium length broadening to blend into the body and free from throatiness.
Forequarters: The shoulders are strong, sloping, muscular and well angulated to the upper arm and should not be too closely set at the point of the withers. The forelegs have strong, round bone, extending to the feet and should be straight and parallel when viewed from the front, but the pasterns should show flexibility with a slight angle to the forearm when viewed from the side. Although the shoulders are muscular and the bone is strong, loaded shoulders and heavy fronts will hamper correct movement and limit working ability.
Body: The length of the body from the point of the breast bone, in a straight line to the buttocks, is greater than the height at the withers, as 10 is to 9. The topline is level, back strong with ribs well sprung and carried well back not barrel ribbed. The chest is deep, muscular and moderately broad with the loins broad, strong and muscular and the flanks deep. The dog is strongly coupled.
Hindquarters: The hindquarters are broad, strong and muscular. The croup is rather long and sloping, thighs long, broad and well developed, the stifles well turned and the hocks strong and well let down. When viewed from behind, the hind legs, from the hocks to the feet, are straight and placed parallel, neither close nor too wide apart.
Feet: The feet should be round and the toes short, strong, well arched and held close together. The pads are hard and deep, and the nails must be short and strong.
Tail: The set on of tail is moderately low, following the contours of the sloping croup and of length to reach approximately to the hock. At rest it should hang in a very slight curve. During movement or excitement the tail may be raised, but under no circumstances should any part of the tail be carried past a vertical line drawn through the root. The tail should carry a good brush.
Gait/movement: The action is true, free, supple and tireless and the movement of the shoulders and forelegs is in unison with the powerful thrust of the hindquarters. The capability of quick and sudden movement is essential. Soundness is of paramount importance and stiltiness, loaded or slack shoulders, straight shoulder placement, weakness at elbows, pasterns or feet, straight stifles, cow or bow hocks, must be regarded as serious faults. When trotting the feet tend to come closer together at ground level as speed increases, but when the dog comes to rest he should stand four square.
Coat: The coat is smooth, a double coat with a short dense undercoat. The outer:coat is close, each hair straight, hard, and lying flat, so that it is rain:resisting. Under the body, to behind the legs, the coat is longer and forms near the thigh a mild form of breeching. On the head (including the inside of the ears), to the front of the legs and feet, the hair is short. Along the neck it is longer and thicker. A coat either too long or too short is a fault. As an average, the hairs on the body should be from 2.5 to 4 cms (approx. 1:1.5 ins) in length.
Colour
Blue - The colour should be blue, blue:mottled or blue speckled with or without other markings. The permissible markings are black, blue or tan markings on the head, evenly distributed for preference. The forelegs tan midway up the legs and extending up the front to breast and throat, with tan on jaws; the hindquarters tan on inside of hindlegs, and inside of thighs, showing down the front of the stifles and broadening out to the outside of the hindlegs from hock to toes. Tan undercoat is permissible on the body providing it does not show through the blue outer coat. Black markings on the body are not desirable.
Red Speckle - The colour should be of good even red speckle all over, including the undercoat, (neither white nor cream), with or without darker red markings on the head. Even head markings are desirable. Red markings on the body are permissible but not desirable.
Size
Height: Dogs 46:51 cms (approx. 18:20 ins) at withers, Bitches 43:48 cms (approx. 17:19 ins) at withers
Faults: Any departure from the foregoing points should be considered a fault and the seriousness with which the fault should be regarded should be in exact proportion to its degree.
Note: Male animals should have two apparently normal testicles fully descended into the scrotum.
DNZ No 504
Copyright Dogs New Zealand
01 Jul 2007
Any departure from the foregoing points should be considered a fault and the seriousness with which the fault should be regarded should be in exact proportion to its degree and its effect upon the health and welfare of the dog and on the dog’s ability to perform its traditional work.




